Abstract P292: Concentrations of Endothelin-1 Predict Coronary Heart Disease in Women in a Swedish Cohort Study
- Bledar Daka1;
- Charlotte A Larsson2;
- Margareta I Hellgren1;
- Lennart RÅstam2;
- Per Anders Jansson1;
- Ulf Lindblad1
+Author Affiliations
Abstract
Objecitves: Endothelin-1 has been linked to coronary heart disease (CHD) in retrospective studies. Although prospective studies in subjects with previous CHD also have shown a higher risk for a second event related to higher endothlin-1 concentration, prospective studies investigating the risk of a first event are still lacking. We accordingly aimed to investigate the risk of a first event of coronary heart disease (CHD) associated with concentrations of endothelin-1 in men and women separately.
Subjects and methods: A random sample of 2.818 Swedish men and women aged 30-74 years was surveyed in 2002-2005 (76% participation). Standard questionnaires were used to gain information on medical history and lifestyle and all participants conducted a physical examination. Endothelin-1 collected at baseline was successfully analysed in 2795 subjects (99%). All first events of CHD were retrieved by record linkage with the Swedish Cause of Death and Hospital Discharge Registers. After controlling for proportionality, Cox Proportional Hazards Regression was employed to investigate the associations between endothelin-1 and incident CHD.
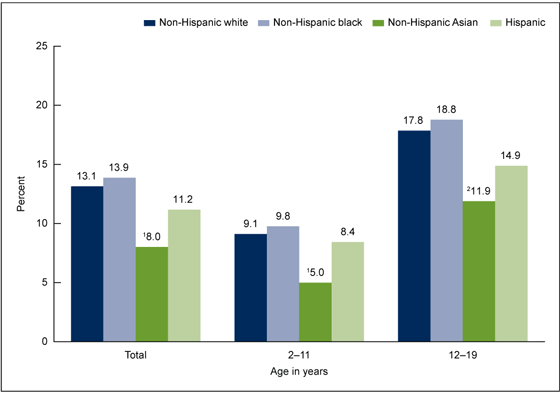
Results: During a mean follow up of 8.1 years (± 0.96) there were 96 incident cases of CHD (men 71 and women 25). Concentrations of endothelin-1 were similar in men and women (2.3 pg/ml vs 2.4 pg/ml p=0.111). In age-adjusted Cox regressions, concentrations of endothelin-1 predicted CHD in women (HR=1.48 CI 1.1-1.8), albeit not in men (HR=1.0 CI 0.9-1.3). These findings remained in multivariable analyses adjusting for diabetes, waist-hip ratio, smoking habits, LDL-cholesterol and systolic blood pressure (HR in women=1.45 CI 1.1-2.0; HR in men=1.1 CI 0.9-1.3). The interaction term between sex and endothelin-1 in the fully adjusted analysis was borderline significant (p=0.055).
Conclusions: Endothelin-1 predicted CHD in women independent of traditional CHD risk factors. If these findings are confirmed in other populations there will be implications for risk evaluation in clinical practice.